India continues to strengthen its climate action framework through a combination of mitigation, adaptation, and resilience-building measures aligned with national priorities and global commitments. The country has adopted a multi-sectoral approach focusing on renewable energy expansion, climate-resilient infrastructure, sustainable agriculture, water conservation, and ecosystem restoration to address the growing impacts of climate change.
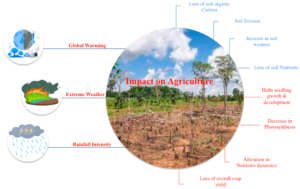
Significant emphasis is being placed on reducing carbon intensity, enhancing energy efficiency, and promoting clean energy sources such as solar, wind, and green hydrogen. Parallelly, adaptation strategies are being advanced to protect vulnerable communities from climate-induced risks including heatwaves, floods, droughts, and extreme weather events. These efforts aim to safeguard livelihoods, public health, food security, and natural resources.
Institutional coordination, scientific research, and data-driven decision-making remain central to India’s climate strategy. Climate early warning systems, disaster preparedness mechanisms, and community-level awareness programmes are being strengthened to ensure timely response and long-term resilience. Public participation and partnerships with civil society organisations are also being encouraged to accelerate climate-positive outcomes on the ground.
Experts underline that sustained climate action requires collaboration between government institutions, local bodies, industry stakeholders, and community organisations. Integrating climate considerations into development planning is increasingly recognised as essential for achieving sustainable growth while protecting people and the environment.